Content Warning
This story contains information about eating disorders including anorexia and bulimia.
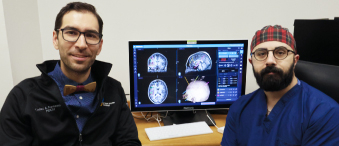
The long-term effects of the COVID-19 pandemic are only now starting to come to light, but mental health is certainly one area impacted the most, including an escalating demand for our eating disorder services, according to Dr. Ruxandra Antochi, Medical Director of the Eating Disorders Program (EDP) at The Ottawa Hospital.
With the help of the Ontario Ministry of Health Roadmap to Wellness, our hospital will work to fill critical gaps in the care of patients with eating disorders, particularly in youth. The EDP is a multidisciplinary program that provides treatment for people with eating disorders such as anorexia nervosa and bulimia nervosa.

“In some ways, the pandemic has increased access to care for patients by taking down the geographical barriers, because virtual care can be accessed from everywhere. Before the pandemic, patients who traveled from elsewhere had to pay for a hotel to stay nearby and be able to attend the Monday through Friday program.”
— Dr. Ruxandra Antochi
It traditionally serves patients in the eastern Ontario region. As Dr. Antochi explains, with services stretched since the pandemic, our EDP has welcomed patients from right across Ontario. “In some ways, the pandemic has increased access to care for patients by taking down the geographical barriers, because virtual care can be accessed from everywhere. Before the pandemic, patients who traveled from elsewhere, had to pay for a hotel to stay nearby and be able to attend the Monday through Friday program.” So, while virtual care is more accessible to patients, the increase in patients also puts increased pressure on the program and staff providing the care.

“When I was growing up, I always wanted to be someone else or look a certain way.”
— Hannah Hotzwik
Eating disorder warning signs
- Unusual preoccupation with weight, food, calories, nutrients, dieting, or exercise
- Eliminating certain foods or restricting whole categories of food
- Abnormal, antisocial behaviour when eating with others
- Strict food rituals (different foods can’t touch, eating only one type of food etc.)
- Skipping meals or only taking small portions
- Noticeable weight fluctuation
- Stomach issues and complaints (reflux)
- Menstrual irregularities (missing periods)
- Poor dental, skin, hair, or nail health
- Extreme mood swings
- Trouble concentrating
- Dizziness when standing
Seeking help during the pandemic
Originally from the Toronto area, Hannah Hotzwik is 20 years old and has been attending Carleton University for two years — in the midst of a pandemic like many other students. Hannah explains she always had body image issues, but the isolation of the pandemic amplified her mental health problems. “When I was growing up, I always wanted to be someone else or look a certain way. Then in the beginning of 2021, I first noticed that this might be an eating disorder. I had some health issues in late 2020 that caused me to lose my appetite, so I wasn’t eating as much and while I didn’t initially think, I’m going to be skinny, it turned into that,” says Hannah.
It wasn’t long before Hannah realized she was looking skinnier and “the way she always wanted to look”. It tied back to the 19 years she spent believing that thinner was better. She then became hyper-aware of what she was eating, her calorie intake, and her activity level. She recalls it being a stressful time and then the situation started a downward spiral. “I had returned to residence in 2021 after the holidays before any of my roommates. I remember thinking this is the perfect opportunity. Nobody will know I was eating as little as possible,” recalls Hannah.
When Hannah’s roommates eventually returned, they were concerned because she was looking very thin. She eventually confided in them saying she may have an eating disorder. A few months later, Hannah was seeking a referral to the EDP at The Ottawa Hospital.
By May, Hannah had her first appointment with Dr. Antochi, who recommended her for the day hospital program, however, the wait would be two to three months. On September 7, 2021, Hannah was accepted into the program. Looking back, she remembers that wait was difficult. “It was hard. It was a lot of emotional drainage and avoidance. I didn’t have the skills yet to get through those times.”
Seeking help during the pandemic
Originally from the Toronto area, Hannah Hotzwik is 20 years old and has been attending Carleton University for two years — in the midst of a pandemic like many other students. Hannah explains she always had body image issues, but the isolation of the pandemic amplified her mental health problems. “When I was growing up, I always wanted to be someone else or look a certain way. Then in the beginning of 2021, I first noticed that this might be an eating disorder. I had some health issues in late 2020 that caused me to lose my appetite, so I wasn’t eating as much and while I didn’t initially think, I’m going to be skinny, it turned into that,” says Hannah.
It wasn’t long before Hannah realized she was looking skinnier and “the way she always wanted to look”. It tied back to the 19 years she spent believing that thinner was better. She then became hyper-aware of what she was eating, her calorie intake, and her activity level. She recalls it being a stressful time and then the situation started a downward spiral. “I had returned to residence in 2021 after the holidays before any of my roommates. I remember thinking this is the perfect opportunity. Nobody will know I was eating as little as possible,” recalls Hannah.
When Hannah’s roommates eventually returned, they were concerned because she was looking very thin. She eventually confided in them saying she may have an eating disorder. A few months later, Hannah was seeking a referral to the EDP at The Ottawa Hospital.
By May, Hannah had her first appointment with Dr. Antochi, who recommended her for the day hospital program, however, the wait would be two to three months. On September 7, 2021, Hannah was accepted into the program. Looking back, she remembers that wait was difficult. “It was hard. It was a lot of emotional drainage and avoidance. I didn’t have the skills yet to get through those times.”
Eating disorder warning signs
- Unusual preoccupation with weight, food, calories, nutrients, dieting, or exercise
- Eliminating certain foods or restricting whole categories of food
- Abnormal, antisocial behaviour when eating with others
- Strict food rituals (different foods can’t touch, eating only one type of food etc.)
- Skipping meals or only taking small portions
- Noticeable weight fluctuation
- Stomach issues and complaints (reflux)
- Menstrual irregularities (missing periods)
- Poor dental, skin, hair, or nail health
- Extreme mood swings
- Trouble concentrating
- Dizziness when standing
Entering the Eating Disorder Program
After the initial consultation at the hospital, there are three options of care: the patient can be admitted to the inpatient program at the hospital, enter the day hospital program, or they can be given community-based resources.
As part of the programs, and under the guidance of a dietitian, patients are offered a meal plan they are expected to follow and complete each day. Patients also take part in skill building including through cognitive behavioral therapy, dialectical behavioral therapy, and nutritional education.
“Learning to build these skills and to be able to use them to deal with intense negative emotions instead of resorting back to the eating disorder symptoms is critical,” explains Dr. Antochi.
Some patients also require medications, especially for comorbid conditions that frequenctly co-occur for someone who’s suffering from an eating disorder. “Most common comorbidities could be depression, anxiety, PTSD, addiction, or personality disorder,” explains Dr. Antochi.
Did you know?





What is an eating disorder?
Eating disorders are serious mental and physical illnesses that involve a complicated and damaging relationship with eating, food, weight, exercise, and body image. They can affect anyone and can often be life-threatening, but recovery is possible.
What is body dysmorphia?
Body dysmorphic disorder (BDD) involves someone having an intense focus on a part of their body, leading to a disproportionate and/or inaccurate view of how they appear. In people with eating disorders, their BDD often focusses on weight.
What is anorexia?
Stemming from Greek for “a loss of appetite,” anorexia nervosa has three main criteria that need to be met for a DSM-5 diagnosis: a restriction of food leading to a significantly lower weight than expected for the individual, an intense fear of gaining weight, and a disturbance in the way the person sees their body.
What is orthorexia?
Named in 1996, orthorexia is not an official diagnosis, but describes a preoccupation with eating in a “healthy” way that becomes obsessive to the point of being disruptive.
What is bulimia?
Bulimia nervosa is characterized by cycles of overeating (binging) and ridding the body of that food through self-induced vomiting, laxatives, or other means (purging). In some cases, people may also excessively exercise or fast (avoid eating food for extended periods).
What is binge eating disorder?
While most people overeat on occasion, binge eating disorder involves eating an unusually large amount of food in a short time, feeling out of control in the moment, and feelings of guilt and shame.
Finding her own voice
Hannah recalls being nervous early on about whether the program would work for her. Her doctors explained this was normal. “At the beginning of the program, your eating disorder voice is so loud. And it’s so controlling that it’s convinced you that you don’t need this. But the point of the program for me was to be able to identify my own voice and what my body and my mind wanted, rather than the disorder,” says Hannah.
For eight weeks, Hannah was enrolled in the day program, which was done virtually. With each week, she progressed in small steps from eating in group sessions to becoming more comfortable with gaining weight. Then Hannah began the post-day hospital Relapse Prevention Program for the next 12 weeks. “The first four sessions are weekly. So, each week, I would talk to one of the nurses and Dr. Antochi. We reviewed what I’ve had to eat that day. And I’d have homework to complete, and we’d go over it together. Then we’d talk about skills and how to deal with things that cause stress, anxiety, and other issues that might lead back to going to my safe space of my eating disorder.”
After completing their program, patients move on to the Eating Disorder Transition Program that continues their care in a community outpatient-based setting.

After completing their program, patients move on to the Eating Disorder Transition Program that continues their care in a community outpatient-based setting.
Grateful for access to care
As Hannah continues her journey, she’s grateful to the EDP for giving her the skills to live a healthier life both physically and mentally. She continues her studies at Carleton University in physical geography and is passionate about climate change and reducing our carbon footprint. “I definitely would not be where I am today without this program. When I look back to before the program, I wasn’t doing well. Now I can confidently say, I’m doing a lot better. I still have challenges and hard days. But the hospital provided me with so many resources and skills that I don’t react the same way as I used to.”
“Now I can confidently say, I’m doing a lot better. I still have challenges and hard days. But the hospital provided me with so many resources and skills that I don’t react the same way as I used to.”
— Hannah Hotzwik
Did you know?
The Ottawa Hospital is a major provider of mental healthcare in the region. “With two psychiatric emergency services, more than 90 beds, a day hospital program, outpatient services, a mobile crisis program, and specialty programs in eating disorders, first episode psychosis and perinatal psychiatry, we are often the first place patients turn to for help,” explains Dr. Jess Fiedorowicz, Head and Chief of our Department of Mental Health.
For Dr. Antochi, there are many others waiting for help and that’s why The Ottawa Hospital wants to expand the Eating Disorder Transition Program to include two additional streams to help meet patient needs. One would be the Eating Disorder Youth (EDY) service in collaboration with CHEO and the other would be the Eating Disorder Readiness (EDR) program which will proactively care for patients awaiting their first assessment or who are currently waitlisted for admission into intensive services by providing them with support and education. “The goals of care in the EDP are centered on patient engagement in collaboration with the healthcare team. It has been inspiring to witness the courage and determination of persons with eating disorders on their journeys towards health improvements and recovery. In addition, it has been a rewarding experience to be part of the EDP team, working alongside colleagues with a strong commitment and dedication towards the best interest of patients’ care,” explains Dr. Antochi.
Who to call for help?
If you or someone you know is experiencing serious mental health problems, call the Mental Health Crisis Line toll free at 1-866-996-0991, or locally at 613-722-6914, 24 hours a day. If you are in immediate danger or a life-threatening situation, call 911 immediately. If you need urgent medical attention go to your nearest hospital.
The Ottawa Hospital is a leading academic health, research, and learning hospital proudly affiliated with the University of Ottawa.