Published: December 2023
The way Katie Skidmore sees it, she was living a normal life for a 36-year-old. She had a full-time job in Information Management/Information Technology, and for four years, she worked for a mining company in Vancouver before moving back home to Ottawa last year to work from home. In April 2023, Katie ran a half-marathon, then only a couple of weeks later was diagnosed with a rare autoimmune disease. The diagnosis would change the course of her life and push her to advocate for advancements in kidney research.
Shortly after her race, while in Calgary on a work trip, Katie started feeling a bit off. “I was feverish and feeling rundown. It was a crazy busy time at work and so that’s what I attributed it to, but then I noticed my urine looked pink,” she recalls. “I didn’t think it was a urinary tract infection (UTI) and my friend suggested I might have a kidney infection.”
She went to a Calgary hospital where some initial tests were done, and they suspected a UTI and prescribed Katie some antibiotics. If symptoms changed, she was to consult her doctor when she returned home. “By the time I got back to my hotel room, I felt even worse and so I booked an earlier flight to Ottawa. Once I was home, I had kidney pain and my urine changed to dark red, so when I landed, I went straight to the hospital.”

Tests revealed a slight decrease in kidney function, so she was monitored overnight. In the morning, her stats improved, and she went home with medication. But when she woke up from a nap, her symptoms had progressed. “I got up to go to the washroom and I couldn’t walk. I also started vomiting.”

Alarm bells would soon sound
The next day Katie made another trip to her local hospital. Doctors advised her to continue her antibiotics. Five days later she returned to the hospital because she had stopped urinating altogether. At this point, she wasn’t alarmed — she believed she was healthy and there would be a solution soon.
But alarm bells would soon ring. Her creatinine levels — which monitor kidney function — had gone from 125 to 1,750 in the span of one week. “I didn’t know what that meant, but I thought, ‘This can’t be good.’ The next thing I knew, I had a catheter inserted and then I was put in an ambulance to be transported to the General Campus of The Ottawa Hospital,” says Katie.
What she didn’t know at the time — but her healthcare team suspected — was that her kidneys were failing because of an autoimmune disease.
“It was a Saturday night. I had many injections, there was a line put in my chest, and they did a biopsy of my kidneys,” remembers Katie. “I wouldn’t be able to start dialysis until Monday, but I was like ‘Rock on – get me better and out of here. I have a trip to France planned that I’ve got to get to.’ I was clueless of the severity of what I faced.”
Faced with a rare autoimmune disease
Within a couple of days, Katie was diagnosed with anti-glomerular basement membrane (anti–GBM) disease. She had never heard of it and admits she had a very delayed reaction to the news and what it meant for her future.
“It hit especially hard when I realized my kidney function likely wouldn’t come back. It was horrific news to try and digest. My life is changed forever. I see it as the girl who flew to Calgary and never came back.”
What is anti-GBM disease?
Previously called Goodpasture disease, anti-GBM disease occurs in fewer than one in a million people. The exact cause of anti-GBM disease is unknown, but it can be triggered by viral respiratory infections or exposure to chemicals, such as through breathing in hydrocarbon solvents or smoking cigarettes.
Symptoms usually, but don’t always, develop quickly. Treatment involves stopping the production of antibodies, removing the antibodies from the blood, and reducing inflammation. The fast development of the disease means it can cause severe kidney damage before it’s diagnosed. In these cases, dialysis is often required.
The following months were beyond difficult for Katie. Mentally and physically, she felt like a completely different person. “I didn’t recognize the person I saw in the mirror.”
According to Katie, doctors call anti-GBM the worst of the worst for kidney disease. “It comes in out of nowhere and it kills your kidneys in days or weeks,” she explains. “It will leave your body in a few weeks or up to two years and never come back but does its damage. It leaves when there’s nothing else to kill.”
Katie’s been told the disease will likely be gone from her body in six to 12 months — it’s trending down but still active now.
After a week in the hospital, Katie went home with her parents and started to put the pieces together about what her new life would look like — dialysis three days a week and no cure for the kidney disease. That’s what led her to want to create more awareness for this illness and kidney research.
“I depend on medical intervention to stay alive, so I need to get the word out that kidney disease is prevalent,” says Katie. “Once you’re on dialysis, it’s for life. I want the world to know, I’m never cured. I’m not in remission. I’m a kidney disease patient for life.”
What kind of kidney research is happening at The Ottawa Hospital?
It’s for that reason, Katie hopes to see research advancements in kidney disease. While there is no cure, there is significant research happening at our hospital to better understand it and hopefully find a cure.
Dr. Manish Sood is a senior scientist, nephrologist, and former Jindal Research Chair for Prevention of Kidney Disease at The Ottawa Hospital. He recently published a study of more than eight million adults in Ontario that suggested even a modest loss of kidney function is associated with increased health risks. This could result in better ways to prevent chronic kidney disease and related conditions, especially for younger adults.
“The dogma is that healthy, young adults don’t need to worry about kidney function unless it drops to around 50% of the normal level,” explains Dr. Sood. “But our research suggests that even a more modest 20-30% drop may have consequences, and we may want to have earlier conversations about prevention and monitoring.”
When it comes to prevention, researchers are attempting to engage the community. Dr. Sood and his colleagues have developed an online calculator that can estimate a person’s risk of developing chronic kidney disease. Early-stage chronic kidney disease has no symptoms, and its onset can often be reduced with lifestyle modifications such as diet, exercise, and quitting smoking. This calculator may improve awareness and help people reduce their risk.

“Our goal is to improve awareness of chronic kidney disease and to empower and personalize care for patients. Our calculator is a simple tool that can be completed by anyone without prior medical knowledge or blood work.”
Care for dialysis patients across eastern Ontario and beyond
Katie began her in-centre hemodialysis treatments at the General Campus and then in June, moved over to the Riverside Campus. She quickly learned what a drastic change this was going to be for someone who was always on the move — now she would be a frequent flier at the hospital.
The nephrology program at our hospital provides care to residents of Ottawa and most of eastern Ontario who suffer from kidney disease. It also serves as a referral centre for the Renfrew and Sudbury area. The Ottawa Hospital’s nephrology program is one of the largest in Canada and offers a broad range of services to those affected by this illness.
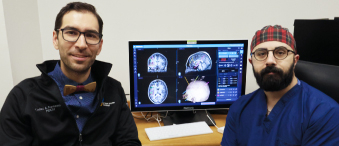
With the expertise of her care team, Katie felt she was in good hands. “There are really supportive people at dialysis — the care team is amazing.” But she admits, as a young patient, she didn’t see many people her age. “For example, I sat next to a 75-year-old gentleman who was great, but he said ‘I’ve lived my life. I can accept this, but I wouldn’t if I were you.’”
It’s conversations like that one, the support of the dialysis team, and Katie’s desire to be more independent, that led her to explore home hemodialysis. She started with a chest catheter implanted to start, and then training began. Her weeks were busy in preparation. “It’s 12 hours of therapy and then 12 to 13 hours of training for home hemodialysis — that started in mid-September. You learn everything from how to set up your machine, connect yourself, troubleshoot if there are issues, do your blood work, change your dressing, and disconnect,” explains Katie.
It takes a lot for a patient to prepare for, but the hospital provides all the support required so that patients can live more independently, which is exactly what Katie has hoped for.

“I feel mentally prepared for it now. I feel physically capable. My blood pressure is under control. I can look at the line in my chest without crying.”
With everything set up in her home, Katie completed her first home hemodialysis in mid-October. She continues to be cared for by Dr. Deborah Zimmerman and Dr. David Massicotte-Azarniouch — one focused on her kidneys and the other focused on the anti–GBM.

Awaiting a kidney transplant
It’s expected she will be ready for a kidney transplant this summer — she just needs a kidney first. Katie is on a kidney transplant list, and she has people stepping forward to see if they could be a living donor.
As she adjusts to her new life, she is determined to plan for her future. “I have more life to live. I want to travel more, especially internationally. I’ve investigated Dialysis at Sea — cruise ships that offer nephrology care. I want to live my life as much as I can.”
But Katie is also here to remind people that she is still not better — her life is completely different today compared to six months ago.
“When people saw me acutely sick, and they see me now going to the gym and travelling across the country, they say it’s so amazing to see you healthy. But I’m not healthy. I’m on dialysis three days a week,” she says.
"I want to project that I’m healthy, I don’t want anyone to forget that I’m part human, part machine. For 15 hours a week I require a machine to keep me alive.”
And so, she moves forward, as an advocate for kidney disease and a desire to push the boundaries of kidney research for her and others like her.