Published: March 2026
Read time: 3 min
Published: March 2026
Read time: 3 min
Kidney disease is often silent in its earliest stages, quietly damaging the body long before symptoms present themselves. By the time traditional tests detect it, the kidneys have already experienced irreversible damage. Roughly 1 in 10 people live with kidney disease, and many are unaware they are at risk.
Dr. Dylan Burger, a senior scientist at The Ottawa Hospital, is working to change that. Thanks to donor support through an ELEVATE seed grant, he and his team are developing ways to detect kidney stress as it happens and to protect these vital organs before lasting damage occurs.
Why the kidneys matter
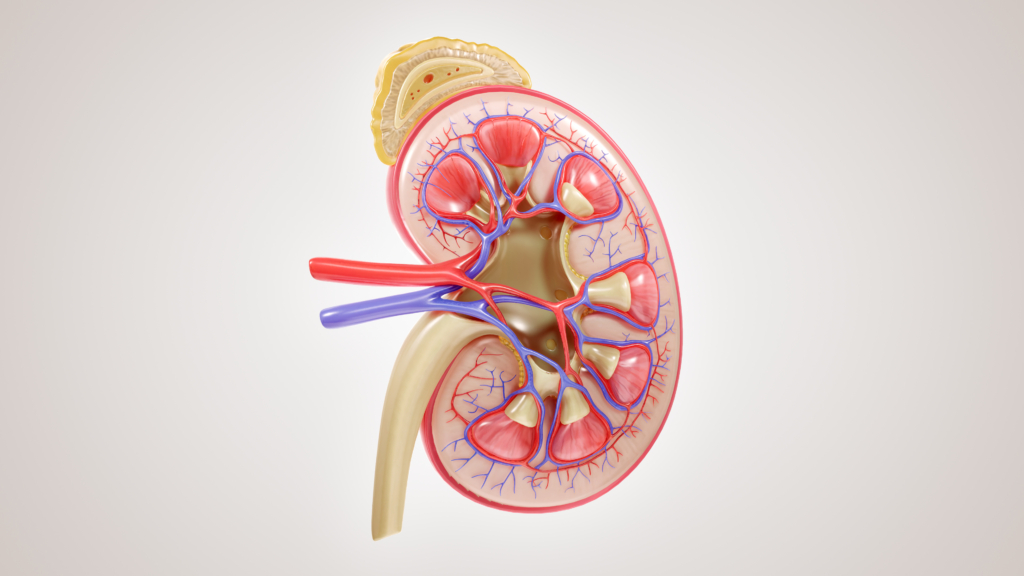
The kidneys do far more than filter waste from the blood. Every minute, they carefully regulate blood pressure, balance fluids and electrolytes, produce hormones that support red blood cell production, and help maintain healthy bones and muscles.
When kidney function begins to decline, the effects are felt throughout the entire body — often before a diagnosis is even made. Rising blood pressure, anemia, fatigue, muscle weakness, calcium and vitamin D deficiencies, and fluid buildup can all signal that the kidneys are under strain. Over time, declining kidney function can also contribute to a higher risk of bone fractures and heart disease.
Kidney disease doesn’t occur all at once. It typically develops over time, beginning with subtle cellular stress before progressing to chronic kidney disease, if left untreated. In severe cases, it can lead to kidney failure, which requires regular dialysis or a kidney transplant to survive.
“Earlier insight gives us more options,” says Dr. Burger. “And more options can mean a very different future for patients.”
Tiny messengers with big potential
At the centre of Dr. Burger’s research are extracellular vesicles — tiny particles released by kidney cells and passed into the urine. These act as biological messengers, providing information about the health of kidney cells in real time.
“When kidney cells are stressed or injured, they release very specific vesicles,” explains Dr. Burger. “In studying those signals, we can gain insight into what’s happening in the kidney long before traditional tests show there is an issue.”
His team has discovered that when specific kidney cells called podocytes are damaged, they release vesicles with a distinct size and characteristics. These vesicles act as early warning signs, flagging kidney injury at a stage when damage may still be reversible.
While some vesicles indicate injury, others have the power to play a protective role. “Cells also release beneficial vesicles that promote regeneration and the health of the cells around them,” explains Dr. Burger. He notes his team is also looking at ways to harness these cells to repair and protect the kidney from further damage.
Meet Dr. Dylan Burger
From the lab to the bedside
For people living with kidney disease, the consequences are often life-altering. Dialysis can require hours of treatment multiple times a week, if not every day. Transplant eligibility depends on timing, overall health, and availability of donor organs. That’s why Dr. Burger’s research is so critical.
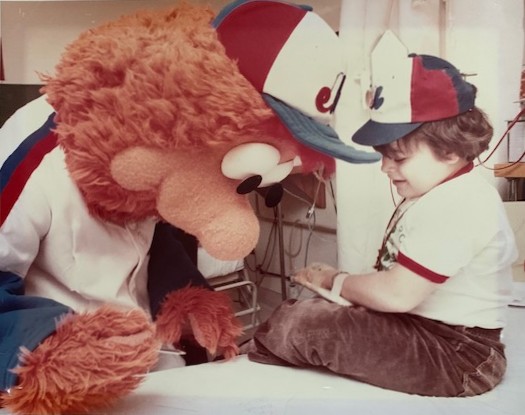

Research like this has the potential to change what a kidney disease diagnosis means for patients like Mauro Burri. For Mauro, kidney disease didn’t just affect his health, it shaped his entire life. Diagnosed more than 51 years ago, Mauro has lived with kidney disease since he was just five years old. Kidney disease can have many causes, but at the time, doctors were unable to determine what led to Mauro’s.
“The hope is that research like this could change the future for patients, so that kidney disease doesn’t have to define someone’s life.”
— Mauro Burri
Over the decades, Mauro’s life has been marked by treatments; years on dialysis, including both peritoneal and hemodialysis; and the hope and uncertainty that comes with transplant surgery. “Even a successful transplant is not a cure,” explains Mauro.
He reflects on long hours hooked up to dialysis machines and the uncertainty of waiting for a compatible donor kidney. Today, Mauro is living with his third transplanted kidney — a reminder of the resilience required of patients and the ongoing challenges they face, both physically and mentally. His journey reflects the long and unpredictable path of many kidney disease patients.
This is where Dr. Burger’s research is transformative. His work could help patients like Mauro avoid years of dialysis, delay or even prevent the need for transplant, and maintain their quality of life.
Changing the course of kidney disease for the next generation
For someone who has lived with kidney disease for more than half a century, the implications are significant for Mauro. “The hope is that research like this could change the future for patients, so that kidney disease doesn’t have to define someone’s life,” he says.
“It feels good to give back and support research that could change the course of kidney disease for the next generation.”
— Mauro Burri
Mauro has also been actively involved in helping raise funds for kidney research, supporting work like Dr. Burger’s through The Kidney Foundation of Canada’s La Serata Italiana gala, which helps generate both funding and awareness for The Ottawa Hospital’s Kidney Research Centre. Established in 2000, the Kidney Research Centre is Canada’s first research facility devoted exclusively to investigating diseases that attack the kidney.
“It feels good to give back and support research that could change the course of kidney disease for the next generation,” says Mauro.

National recognition for groundbreaking work
Dr. Burger’s work is gaining national attention. He is the most recent recipient of the Dr. John B. Dossetor Research Award from The Kidney Foundation of Canada, one of the country’s most prestigious honours for his line of work. The award recognizes excellence, leadership, and innovation that advance the future of kidney care.
While he is incredibly grateful, Dr. Burger remains focused on what lies ahead. “The real impact,” he says, “is what this research could mean for individuals impacted by kidney disease.”
Advancing discovery in kidney care
Innovative kidney research projects, like Dr. Burger’s, have received critical early-stage funding through the Ottawa Hospital Research Institute’s ELEVATE seed grants, funded in part by donor support to The Ottawa Hospital Foundation. These grants help researchers test bold ideas that may one day improve the lives of patients, not only in Ottawa, but globally.
Donor support has also played a vital role in advancing kidney research by helping scientists push boundaries, train the next generation of researchers, and translate discoveries from the lab to the clinic faster than ever before.
For Dr. Burger, that support fuels his goal of changing what a kidney diagnosis could mean for patients. “If we can identify kidney stress earlier and protect the kidneys before damage becomes permanent,” he says, “we can give people a much better quality of life. It would be life-changing.”