Update: In early 2023, Dr. Thébaud’s team treated the first baby in their clinical trial that aims to prevent BPD in premature infants. This is the first trial of its kind in in the world. Read Dr. Thébaud’s Q&A to learn more about his critical work and what motivates him.
Published: August 2020
Little Olivia Eberts had oxygen tubes in her nose until after her first birthday. Because she was born prematurely, her tiny lungs were underdeveloped, and she couldn’t breathe without oxygen. Ironically for Olivia, and many premature babies like her, the oxygen that saved her life also damaged her lungs, causing bronchopulmonary dysplasia (BPD), which is like starting out life with emphysema. But a clinical trial at The Ottawa Hospital led by Dr. Bernard Thébaud, which uses stem cells to heal the lungs of premature babies, may be a game changer.
An unexpected early birth
Jamie Eberts was 22 weeks pregnant with twins when she started feeling some discomfort. She arrived at the General Campus of The Ottawa Hospital and was admitted — she was going into early labour.
Thankfully, the doctors and nurses at The Ottawa Hospital were ready for any scenario Jamie, her husband Tim, and the babies faced. Each day, there were gentle conversations about how the babies were doing, the process of delivering them, and the chances of survival. Every hour counted. Then, one of the babies developed an infection and all three lives were at risk — the babies had to be delivered.
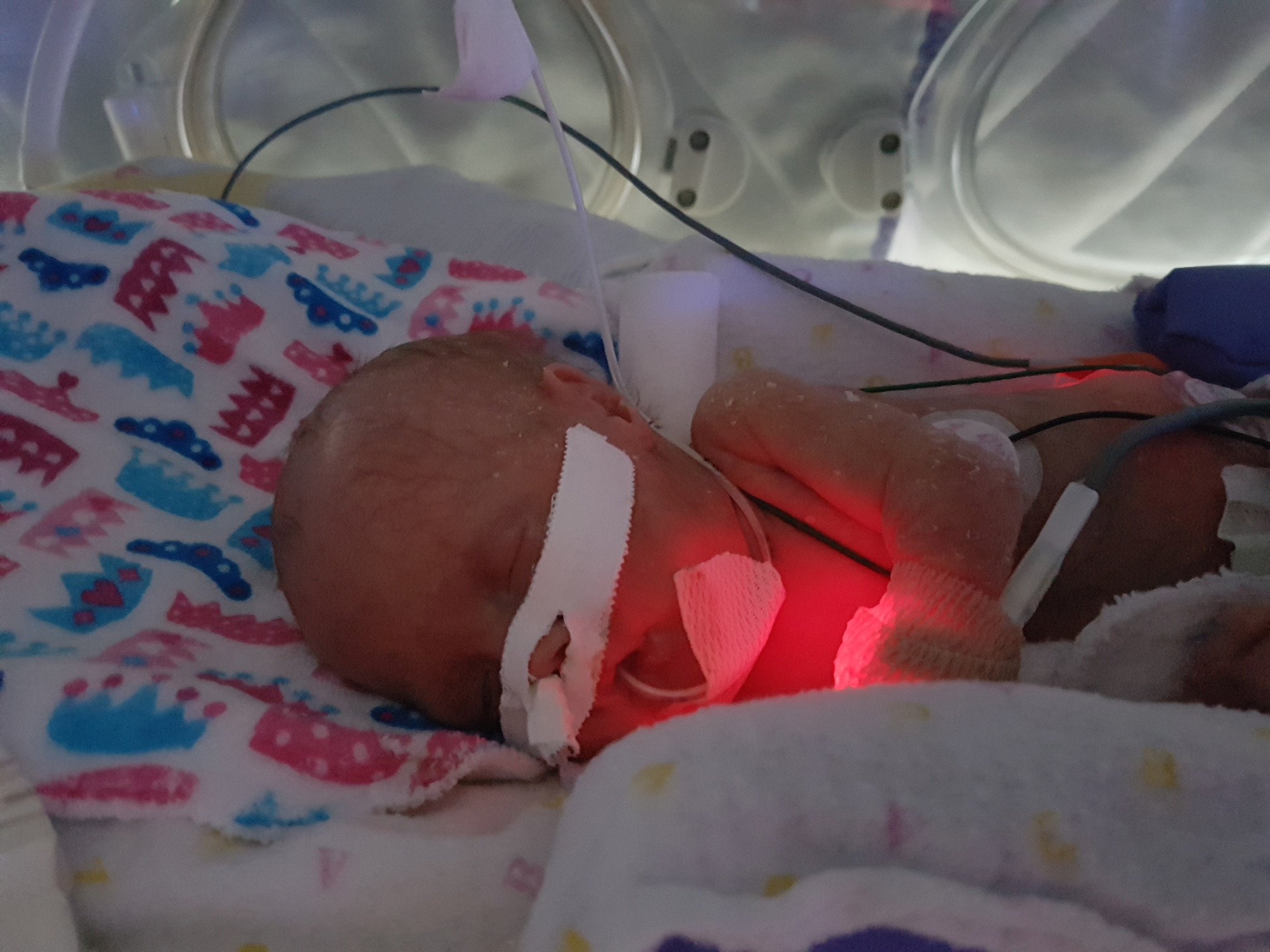
“Our babies, Liam and Olivia, were born at 5 a.m. on January 29, 2017, at 23-and-half-week’s gestation. Liam was born first. He was small, red, and didn’t make a sound,” remembers Jamie. Olivia weighed one pound, two ounces and Liam weighed only a few ounces more than she did. Both babies required oxygen and mechanical ventilation to keep them alive. As a result, both developed BPD — the most common cause of death in premature babies.
Sadly, baby Liam passed away a few weeks after he was born while Olivia remained in the Neonatal Intensive Care Unit (NICU) at The Ottawa Hospital for nine long months.
BPD in Canada

In Canada, 1,000 babies are diagnosed with BPD every year. Often, babies with BPD develop other chronic lung diseases, such as asthma, and many require prolonged oxygen and ventilation. Additionally, they have a high incidence of hospital readmissions in the first two years of life. Babies with BPD often have problems in other organs as well, such as the brain or the eyes.
When Olivia was finally discharged, she went home with an oxygen tank. During the first year of her life, Olivia spent more time in hospital than out.
“Even now, a simple flu that put me in bed for a couple of days put her in hospital and turns into pneumonia. It’s scary,” says Jamie. The doctor told her that with Olivia’s respiratory issues, she may require hospital intervention for the rest of her life.
Lack of treatment options
“Currently there is no treatment for this disease,” says Dr. Bernard Thébaud, a neonatologist and senior scientist at The Ottawa Hospital. With that being said, he’s determined to improve the outcome for babies, like Olivia, who have BPD.
“In the laboratory, we discovered that a particular type of stem cell can prevent BPD or regenerate newborn lungs.”
— Dr. Bernard Thébaud

“Our research uses stem cells, isolated from the umbilical cords of healthy newborns, to prevent the lung injury or even to some degree regenerate a damaged lung in the laboratory. We foresee that these stem cells, given during a certain time during the hospital stay of these babies, could prevent the progression of the lung disease.”
Unlike traditional stem cells that can directly replace damaged cells and tissues, the stem cells that Dr. Thébaud is studying work by producing healing factors that promote regeneration and repair.
Clinical trial offers hope
Dr. Thébaud and his research team have launched a phase I clinical trial to test the feasibility and safety of the stem cell treatment in premature babies. The team is doing everything in their power to make this clinical trial a success, including consulting with healthcare providers and parents of premature babies.
One thing they’ve learned from these consultations is that many parents don’t feel like they know enough about stem cells and clinical trials to decide if they want to enroll their child in the trial. So, Dr. Thébaud and his team created an animated video to explain these concepts and help parents make an informed decision. Parents can share the video with family members if they’d like a second opinion.
Jamie was involved in these consultations and her firsthand experience provided valuable insight to the research team as they planned this project. This is just one example of how researchers at The Ottawa Hospital are partnering with patients and caregivers to improve the quality and success of their research.

Dr. Thébaud and his team held a “dress rehearsal” for the clinical trial. “The dress rehearsal lets us test and tweak our tools for approaching parents, including the video, so we know what works best once we’re ready to begin offering the experimental treatment.”
If this initial trial is successful, Dr. Thébaud and his team will launch a larger Canadian clinical trial. “This is a critical step towards providing a potential breakthrough therapy that could help premature babies in Canada and around the world,” says Dr. Thébaud.
The made-in-Ottawa clinical trial is supported by The Ottawa Hospital’s Ottawa Methods Centre and Biotherapeutics Manufacturing Centre, and the Blueprint Translational Research Group.
First trial of its kind in Canada
“Stem cell research is incredibly innovative. Here, we have a very promising, emerging therapy that could prevent lung injury but also improve brain development and eyesight,” says Janet Brintnell, Clinical Manager of the NICU who has seen dozens of premature babies with BPD.
“It’s amazing when you think of what it may be able to do for the quality of life for the child, for their family, and for our healthcare system. It could reduce length of stay, hospital admissions, and improve long-term outcomes. It could help these little ones lead healthier lives.”
— Janet Brintnell
“We are the only ones doing this kind of stem cell research in Canada, and there are only a few other teams in the world that are doing this.”
— Dr. Bernard Thébaud
Yet, three years ago when Olivia was in the NICU, this treatment wasn’t yet available. Now, Jamie and Tim are self-described “cheerleaders” of Dr. Thébaud’s research and are hopeful for what it might mean for future preemies and their families.
“I believe this is our future,” says Jamie. “When I think about what this could have done for our family, I wonder if Liam could have possibly survived. Olivia may not be facing the delays she’s experiencing today. Even to this day, if we are asked to put Olivia in the trial as an older candidate, we will.”
Jamie also adds the there was an impact from a mental health and financial perspective. “Our oldest child, Jacob, has had a very unusual first four years of his life because of how adaptable he has had to be during these difficult times. As a family, this entire experience has been very challenging financially due to a variety of therapies for Olivia and having to get used to becoming a single income family for several years in order to manage Olivia’s complicated schedule. All of this could have potentially been avoided if Dr. Thébaud’s research were available to our twins.”
A new beginning
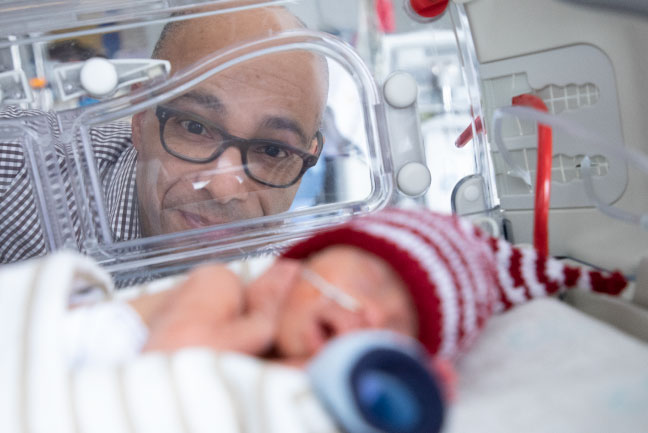
Olivia is now a happy, active toddler who loves copying what her older brother Jacob does. Although, she still has BPD, it is increasingly manageable, and she no longer requires supplemental oxygen. While Olivia may suffer respiratory illness her entire life, one day a stem cell treatment developed here in Ottawa could mean that the next generation of babies with BPD won’t.

Listen to Pulse Podcast and learn how one day stem cells could heal the lungs of premature babies with Dr. Bernard Thébaud and what it could mean for parents like Jamie Eberts.
The Ottawa Hospital is a leading academic health, research, and learning hospital proudly affiliated with the University of Ottawa.