Three years ago, Sandy Patenaude was given the devastating news that she had stage 4 colorectal cancer. It had spread to her liver and lungs, and was inoperable. Sandy’s oncologist asked if she would like to go on a clinical trial, testing a new cancer stem cell inhibitor drug along with her chemotherapy.
“Cancer stem cell inhibitors, why not?” said Sandy who agreed to be part of the trial.
Dr. Derek Jonker, Medical Oncologist at The Ottawa Hospital, is leading the international trial for people with colorectal cancer, with the experimental drug napabucasin. He explained that cancer stem cells are the rare, immature cells in a tumour, which are often resistant to chemotherapy. They can give rise to the more mature cancer cells that make up the bulk of a tumour. Cancer stem cells are not the same as the normal stem cells that live in many healthy adult tissues and help with healing and repair.
“With chemotherapy, we can deliver treatment that can shrink the vast part of the cancer,” said Dr. Jonker, who is also an associate professor at the University of Ottawa. “Often the bulk of the tumour disappears, but what’s left is a small tumour with lots of these chemo-resistant cancer stem cells, which are able to spread and seed other places in the body. Often, we keep giving the same chemotherapy and find the tumour has regrown, but it’s not the same tumour it was when we started.”
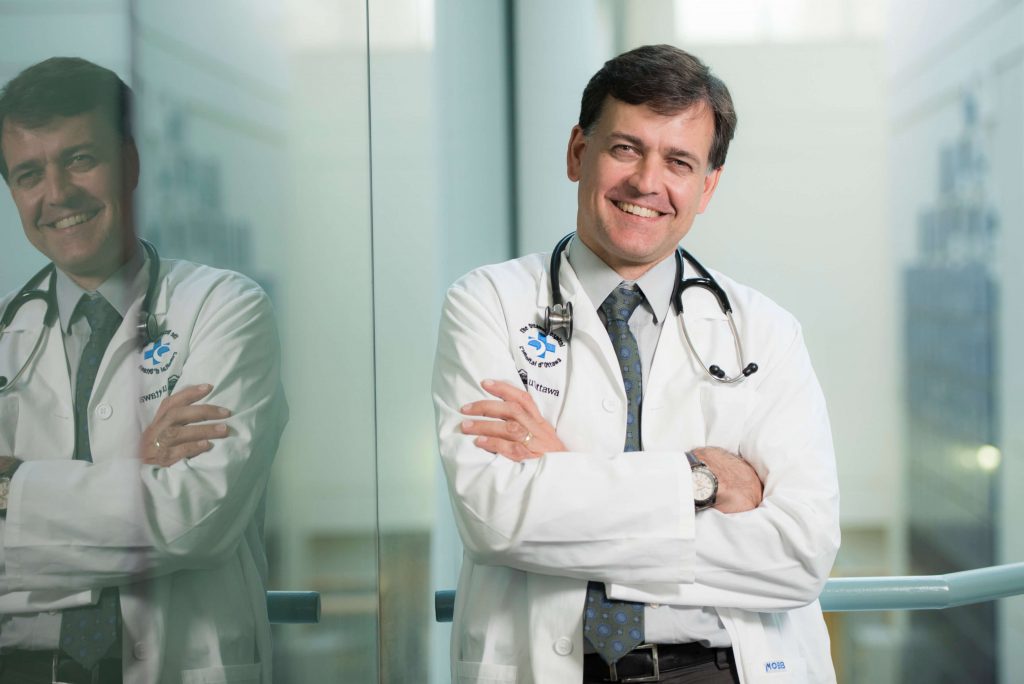

Dr. Jonker is switching up the treatment to target the cancer stem cells that aren’t affected by standard chemo. In a previous randomized clinical trial he led , patients either received a placebo or napabucasin to test its effectiveness at inhibiting, or preventing, the growth of the cancer stem cells. The trial was carried out at 40 sites in Canada, Australia, New Zealand, and Japan. The 562 patients enrolled had advanced colorectal cancer and chemotherapy no longer worked for them.
Looking at the results of the trial, Dr. Jonker said they didn’t see much benefit in the group overall. “But when we looked at patients who had a tumour that had characteristics of a high cancer stem cell (phospho-STAT3) over expression there was very significant improvement in their survival.”
Dr. Jonker presented his findings in October 2016 at the European Society for Medical Oncology, showing that where the cancer stem cell inhibitor didn’t work in all patients, there was an improvement in the survival of the 22 percent of patients who had tumours with high phospho-STAT3. He said it’s “proof of principle that stem cells are an important target for cancer patients.” Napabucasin is now being combined in the current trial with chemotherapy to attack the cancer on two fronts at the same time.
“We know with results of the clinical trial that the majority of patients did not respond to it, but we have two patients here in Ottawa who have responded and definitely developed benefit from the clinical agent,” said medical oncologist Dr. Christine Cripps.

I thought I’d be part of the trial, because I thought well, it’s new.”
Sandy is one of those patients who benefited. Her tumours shrank, and the surgeons were able to remove spots in her liver and the primary tumour in her rectum. Dr. Cripps said she believes that part of the success in keeping Sandy’s cancer at bay is the napabucasin she is taking as part of the clinical trial.
“A stem cell inhibitor works differently than traditional chemotherapy, in that it prevents new disease from appearing,” said Saara Ali, research coordinator for clinical trials in gastrointestinal cancers. “The hope is that the pill [napabucasin] will prevent new disease from showing. And in Sandy’s case there hasn’t been new disease since her treatment. Everything was there before, so it may be doing its job.”
Next steps: Dr. Jonker hopes to start another clinical trial with the cancer stem cell inhibitor that will be used specifically for patients who have lots of phospho-STAT3 in their tumour. These patients could be identified for the clinical trial with molecular testing, using The Ottawa Hospital’s Molecular Oncology Diagnostics lab. This would target the patients presumed to be the most likely to benefit most from the drug.
“We would repeat our study, randomize those patients with napabucasin and a placebo, and if we can prove that napabucasin is effective for them, then it would be an option for patients who have run out of all other treatment options,” said Dr. Jonker.
Dr. Cripps said that Sandy is a candidate for this next trial, and her tumours will be analyzed by the molecular lab to see whether she has high phospho-STAT3 cancer stem cell expression. Regardless, Sandy will continue using the trial drug as long as it is working for her. And it is working. The mother of three adult children said she’s busy doing a million things, playing euchre, the ukulele, skiing, hiking, biking, and enjoying life.
The Ottawa Hospital is a leading academic health, research, and learning hospital proudly affiliated with the University of Ottawa.