Lukas Marshy takes us on his journey of the night he arrived at The Ottawa Hospital in distress and extreme pain. He needed specialized care from our neurosurgery team for a rare condition that resulted in a massive brain hemorrhage. Here is Lukas’ story in his own words.
It was late afternoon on a cold winter January day in 2012 when I was rushed to The Ottawa Hospital. Something was very wrong. That was ten years ago — but it’s a time in my life I will never forget.
I was 16 years old at the time and was playing video games — nothing out of the ordinary for a teenage boy. I remember I reached down to plug in the speaker for my computer and I felt dizzy — the room around me started spinning. I also realized I had a headache, and it was pretty bad.
I went upstairs to let my dad know, and he initially thought I was coming down with something. He gave me some Tylenol for the headache, and I went to lie down in my room. But when I looked up at the ceiling, it was spinning — I couldn’t even look at it. I yelled for my dad.
At that point, I thought I was going to be sick to my stomach, and he said, “Let’s get you down to the bathroom.”

Red flags raised
Then I realized I couldn’t stand up — that’s when the red flags went up for my dad. He helped me to the bathroom, and I vomited. I remember clutching onto the toilet because it felt like I was being pulled to one side of the room. It felt like in a movie when someone opens the airplane door and everything gets sucked outside. I was holding on to the toilet bowl so tight.
Eventually, out of exhaustion, I passed out and I was lying on the bathroom floor. I could hear my dad’s voice trying to prompt me to go back to my bed, but I couldn’t respond. He finally said, “If you don’t stand up, I’m going to have to call an ambulance.” And I thought to myself, ‘That’s perfect, I’m going to stay down because I need help.’ I just couldn’t say the words.
“I remember clutching on to the toilet because it felt like I was being pulled to one side of the room. It felt like in a movie when someone opens the airplane door and everything gets sucked outside. I was holding on to the toilet bowl so tight.”
– Lukas Marshy
When the paramedics arrived, they asked lots of questions. They were concerned I had overdosed on drugs or had been drinking, but I knew that wasn’t the case. Eventually, I was able to tell them no.
They got me onto the stretcher, and we headed outside. I remember seeing the snow and feeling the cold on my body as they loaded me into the ambulance. They took me straight to CHEO where a CAT scan of my brain indicated a massive hemorrhage. At this point, doctors recommended that I be transferred to The Ottawa Hospital’s Civic Campus for specialized surgery.
Transferred to The Ottawa Hospital after brain hemorrhage diagnosis
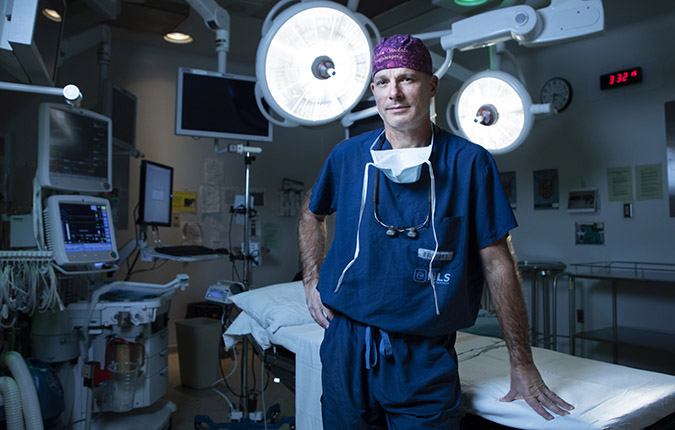
While I was in and out of consciousness, and my memory is a bit spotty, I do remember being in extreme pain. I also remember my mom being by my side. When I think back on that night and arriving at the hospital, that was the worst part of the entire journey — the pain in my head was excruciating.
I was diagnosed with Arteriovenous Malformation (AVM). We learned I was born with an abnormal tangled mass of blood vessels in the back of my head. An intricate surgery by a skilled team was required, and as I waited for them to prep for surgery, I was given medication to ease the pain. That’s the first time I started to feel more comfortable — even though brain surgery was looming.
What is a brain AVM?
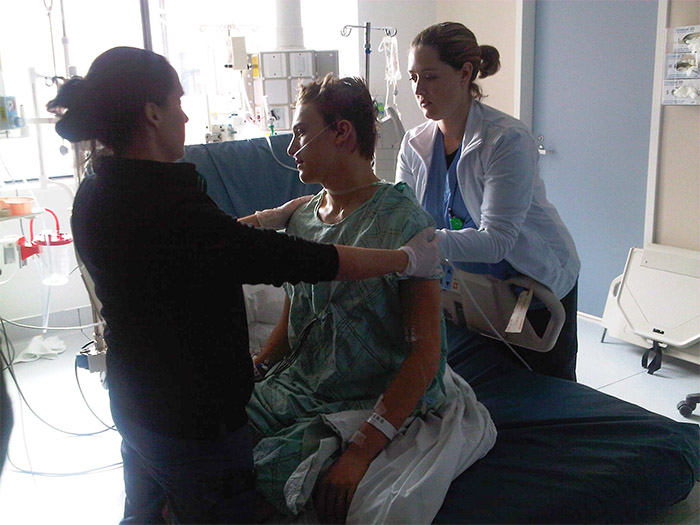
An arteriovenous malformation —or AVM — is an abnormal tangle of the blood vessels connecting an artery to a vein. An AVM disrupts normal blood flow and deprives the surrounding tissue of oxygen. AVMs can occur anywhere in the body, but when they’re in the brain, they’re more likely to cause long-term effects. About 88% of AVMs go undiagnosed, and once diagnosed, brain AVMs can usually be treated to reduce risks.

Normal blood vessels.

An abnormal tangle of blood vessels.
My dad stayed with me the whole time I was in the hospital — he even slept by my side at night. The team caring for me was kind, but having my dad with me was an added level of comfort.
“It was almost as though a calmness came over me. I wasn’t nervous at all because whatever was happening to my brain at the time was going to get better.”
– Lukas Marshy
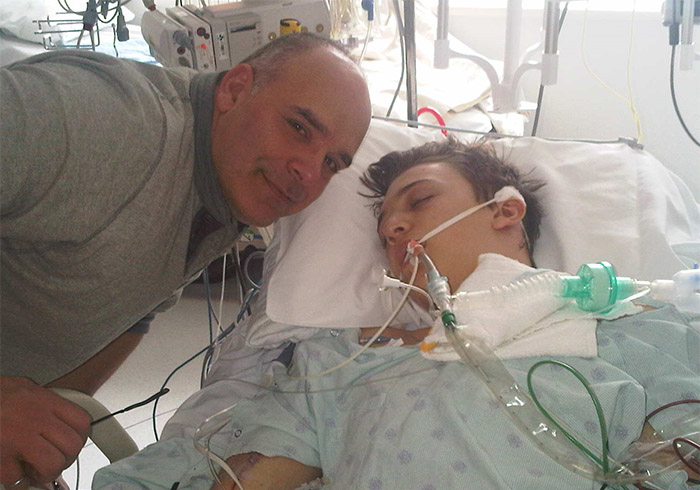
When my dad told me I was going to have brain surgery, I reflected on an actual conversation I had with friends a couple years before. We asked each other “What is a type of surgery you’d never want to have?” If you can believe it, I said brain surgery because that seemed the most dangerous.
But when I was actually faced with that reality, I just remember thinking, “No problem.” It was almost as though a calmness came over me. I wasn’t nervous at all because whatever was happening to my brain at the time was going to get better. I also had Dr. John Sinclair in my corner — he’s amazing.
Facing surgery for a brain hemorrhage
By 7 a.m. the next morning, I was ready for surgery.
It was an eight-hour procedure. The hemorrhage was in the cerebellum area of my brain, so the lower left back side of my head. Dr. Sinclair and his team removed most of the clot, which turned out to be pushing against my brain stem. That was scary to learn, but thankfully it didn’t cause any permanent damage. In fact, Dr. Sinclair explained they left a small portion of the clot there, which they cauterized, because they needed the swelling on my brain to come down before they could remove the clot completely.
The surgery was successful, but I wasn’t done yet. I was placed in a medically induced coma for the first few days, and I remained in hospital for two or three weeks before I could go home. That first homemade sandwich I ate when I got home is something I won’t forget. I think it was the best egg salad sandwich I’ve ever eaten! My siblings were all home with me — and my dog — it was so good to be back.
Road to recovery
On February 28, 2012, I returned to The Ottawa Hospital for the second surgery to remove the malformation which had caused the bleeding. During this operation, the remaining clot and AVM were removed from my brain and Dr. Sinclair placed a titanium mesh about the size of a credit card to replace where a piece of my skull had been removed during the first surgery. Once again, I was put in a medically induced coma for three days, and when I woke up my recovery began.
“To this day, my family says Dr. Sinclair not only saved my life, but he made me smarter too!”
– Lukas Marshy
Next up was physiotherapy to help get my strength back. I was determined to get back home for good, so just over a week later when my care team asked me to show them how I managed the stairs, I tackled those steps with determination. I guess my progress was convincing because after that I was cleared to be discharged.
A whole new perspective on life
I had to use a wheelchair for a short period before progressing to a walker, but as a 16-year-old, I was ready to ditch it as soon as possible. I resumed my schoolwork at home for a few weeks until I was strong enough to get back to the classroom. I was finally reunited with my friends and was able to return to my grade 11 classes.
Something important to note, my marks after the surgery were in the 90s. I was thrilled because, you see, in grade 10, my marks weren’t anywhere near that level. In fact, I usually got 60s and some 50s. So, to this day, my family says Dr. Sinclair not only saved my life, but he made me smarter too!
“The Ottawa Hospital gave me a second chance at life.”
– Lukas Marshy
I’ve been great ever since. I haven’t had any long-term mobility or balance issues — I was incredibly lucky. Lucky that my dad took those first symptoms seriously and called for help. Lucky to have the brilliance of neurosurgeon Dr. Sinclair and the other healthcare providers leading my care. And lucky to be living a normal life today, because if the AVM hadn’t been discovered early after the symptoms started, it may have resulted in serious disability or death because of where it was located.
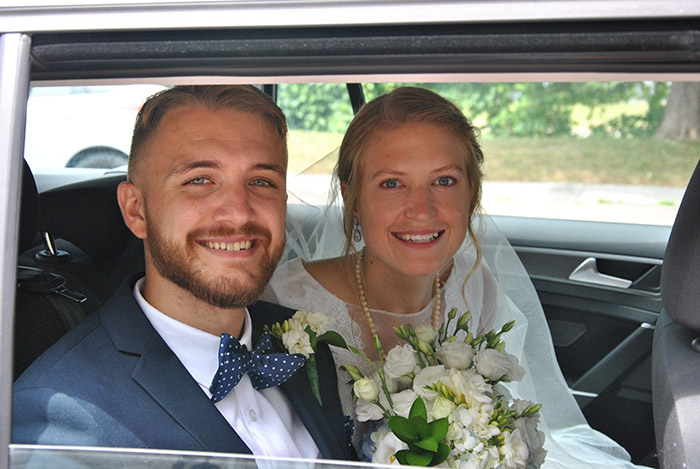


The Ottawa Hospital gave me a second chance at life. Today, I’m married, have two young children, and I have a great job at Queen’s University in Kingston. That experience ten years ago as a 16-year-old changed my whole perspective on life. If this had not happened to me, I wouldn’t be the person I am today. I’ve been cherishing life ever since.
Download episode #64 of Pulse Podcast to hear Lukas Marshy’s story.