What are stem cells?
Every tissue and organ in the body is made up of billions of cells, each with a specialized function. Stem cells are the blank-slates from which all other types of cells originate. They have the ability to divide and make exact copies of themselves or produce specialized cells that can then become new heart muscle cells, brain cells, or other types of cells that can repair damaged organs and tissues.
Two types of stem cells are most commonly used in research:
Pluripotent stem cells
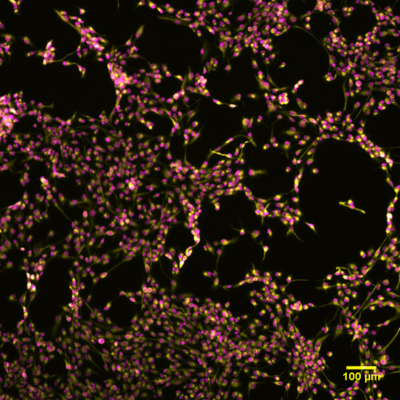
Pluripotent Stem Cells, like embryonic stem cells, are able to produce all the different kinds of cells of the body. Because of recent advances, this powerful stem cell can now be made in the laboratory by genetically reprogramming regular adult cells to make them behave like embryonic stem cells. These ‘induced pluripotent stem cells’ (iPSCs) are commonly used to investigate disease onset and progression, to speed up drug development, and to create new therapies for cell and organ transplant applications.
Somatic or adult stem cells
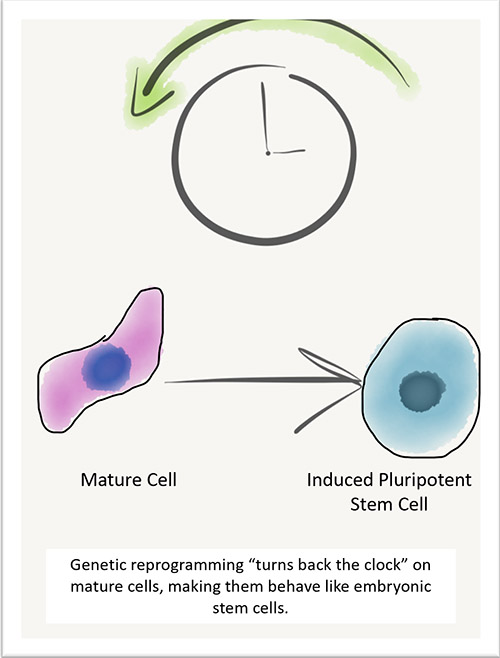
Somatic or adult stem cells are found in most mature tissues and organs. These cells are already somewhat specialized and can only make the kinds of cells found in the original tissue. They may also release biological factors into surrounding tissue, to encourage healing in other ways.
How are stem cells used?
Researchers have found that stem cells can be used to treat injury and disease by stimulating the body to repair itself. An early and common example of a stem cell treatment is a bone marrow transplant. A cutting-edge technique when it was introduced about 60 years ago, there are now more than 50,000 performed worldwide, every year.
Bone marrow transplants replace diseased stem cells, incapable of making normal blood cells, with stem cells derived from healthy bone marrow. These new stem cells grow and reproduce, allowing the marrow to make healthy, new blood cells. These procedures have revolutionized the way we treat blood disorders and cancers of the blood like leukemia or lymphoma.
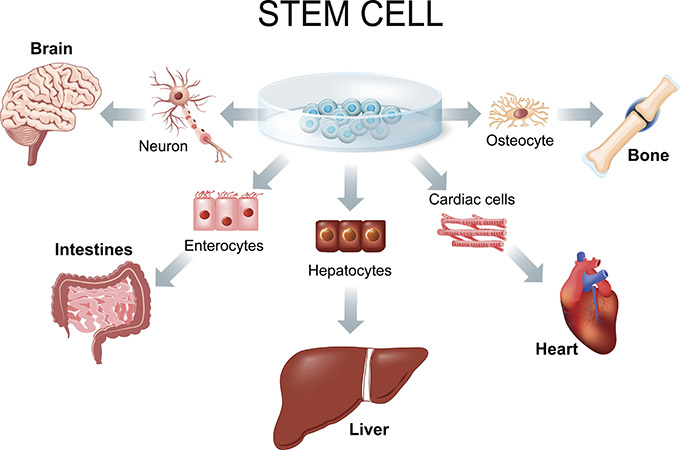
Today, researchers are investigating new ways to use stem cells to rebuild damaged tissue throughout the body, and to treat a wide range of debilitating diseases. In fact, at The Ottawa Hospital our researchers are exploring stem cell therapies for every major system in the human body and we are now using stem cells as a standard treatment for certain kinds of multiple sclerosis.
We are also leading several groundbreaking clinical trials of stem cell treatments for conditions like heart attack, septic shock, COVID-19 and lung damage in premature babies.
How can I access stem cell therapy?
Stem cell therapy is still considered experimental in most cases. If you are interested in stem cell research, you should speak with your healthcare provider to find out if there are any clinical trials that you may be eligible for. You should also be skeptical of anyone who offers stem cell therapies for a fee.