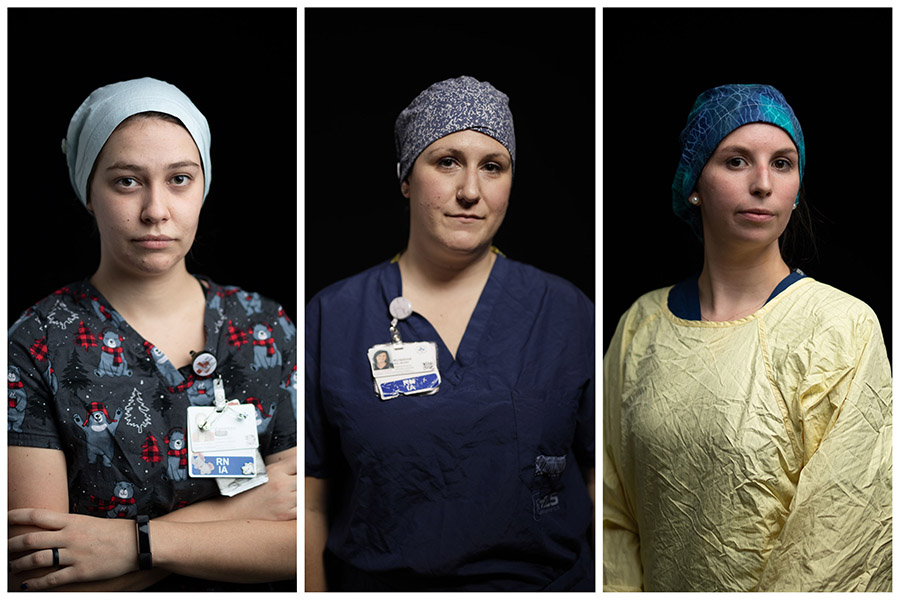When COVID-19 moved into the Ottawa region in March of 2020, we were in uncharted territory. However, despite the rapidly changing information in the early days, and the unknowns about this virus, something very clear began to emerge – unity. The community would soon show an outpouring of support for The Ottawa Hospital while healthcare teams rallied together to care for patients.
“Thank you to our generous donors – some who reached out for the first time.”
– Tim Kluke
As our front-line workers would go into the hospital each day to face the virus head-on, the community stayed home to help flatten the curve. Nevertheless, it became obvious residents wanted to do more – and they did. Donations both big and small began streaming in and the COVID-19 Emergency Response Fund was created. To date, more than $2 million has been generously donated to support our hospital’s COVID-19 efforts and these donations have already been put to work. Tim Kluke, President and CEO of The Ottawa Hospital Foundation, says this support has made a world of a difference supporting both research and care projects. “This proves once again that we really are stronger when we pull together. Thank you to our generous donors – some of whom have even reached out for the first time. Research currently underway will allow us to better understand and treat the virus, to keep our patients and our community safe.” Donations continue to be accepted today.
Personal Protective Equipment (PPE) was another way our community lent a helping hand. The Ottawa Chinese Community quickly mobilized and raised over $120,000 to purchase necessary equipment like ventilators and PPE for our staff.
In Their Own Words: Good Days, Bad Days, and What Keeps Them Coming Back
Stepping into the unknown
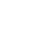
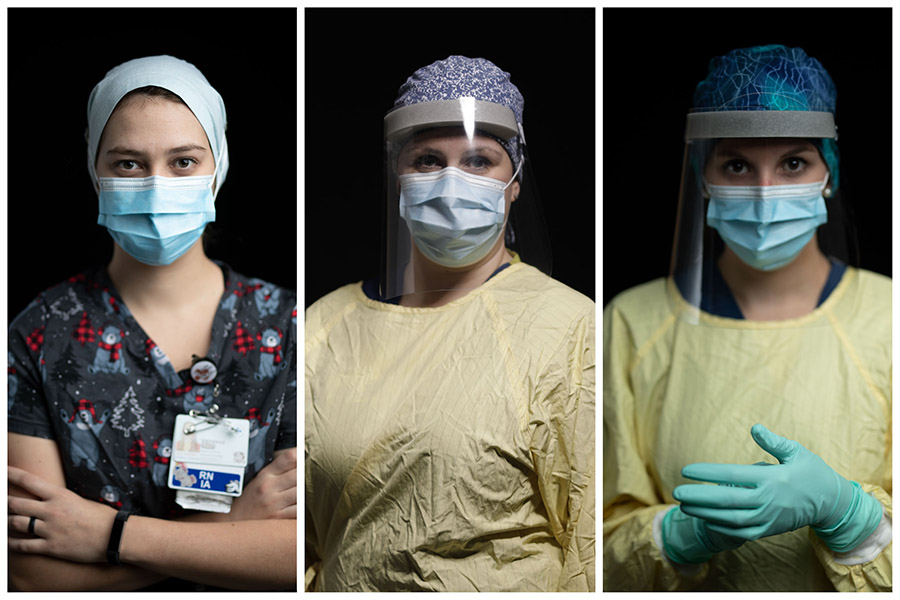
While the community united to show their support for our front-line workers, a COVID-19 floor was created at both the General and Civic Campuses to care for the patients who tested positive for the virus. The team at the General Campus that had originally cared for Thoracic, ENT (Ear, Nose, and Throat), and surgical patients would, almost overnight, become the team caring for COVID-19 patients. Little did they know at the time, they would be caring for these patients for well over a year. “We have a background in lungs and breathing issues on our unit, so we were a natural fit to care for these patients,” says Vanessa Large, a registered nurse at our hospital for the past four years.
Nevertheless, it was a daunting and draining task. Kristine Belmore is a registered nurse who has been at our hospital for 11 years and never did she imagine her career taking this step. “I was working the day the first positive patients came in. We were constantly getting new updates on protocols for caring for these patients – not just daily but during our shifts,” says Belmore. She adds, “It was the equivalent of how I felt when I was a new nurse preparing for a shift — I didn’t sleep well. I was anxious and there was the fear of the unknown.”
Leah Mills was just three years into her career as a registered nurse when she found herself caring for COVID-19 patients. “There was no easing into the COVID transition; it turned our world upside down,” says Leah.
Resilience as weeks turn into months
In those early weeks of caring for patients, there was the struggle of watching some patients go from appearing stable to suddenly clinging to life. Those days would take an emotional toll on these nurses. “The increase in demand during the surge of patients was overwhelming. Over time it became easier because we had concrete policies in place and we started recognizing a pattern in patient’s decline,” recalls Leah.
“We became their only sources of human connection, we became their second family. We would be there holding an iPad so they could see the friendly smile of a loved one – sometimes it was to say goodbye.” – Vanessa Large
The playbook had to be reinvented and new ideas had to be considered to help calm patients when they struggled to breathe or feared what might happen next. Then there were the layers of PPE, which created an additional level of safety but also a new challenge. “Caring for patients, especially the elderly who can be confused, was difficult because they can’t see your facial expressions – we had to find new ways to reassure patients when they were scared. We also became the link between the patient and the family, through phone calls and video calls – something we’ve never done before,” says Kristine.
Vanessa agrees adding, “We became their only sources of human connection, we became their second family. We would be there holding an iPad so they could see the friendly smile of a loved one – sometimes it was to say goodbye.”
Mentally and emotionally, the long haul of this pandemic started to wear on these nurses. Leah explains they’re used to helping patients heal and get better. “We’re feeling burned out and exhausted seeing patients decline quickly and sometimes die. It’s not what I’ve been used to in my role.”
Thankfully, over the past year, this dedicated care team has helped ensure the majority of COVID-19 patients have been able to regain their health and return home to their loved ones.
The nurses of the “COVID floor”

— Leah
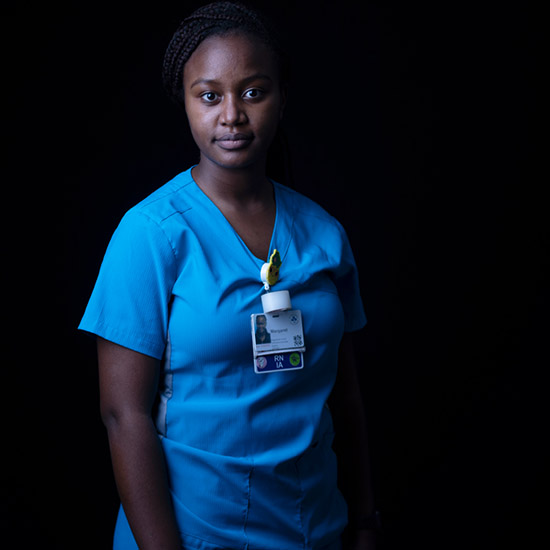

— Margaret
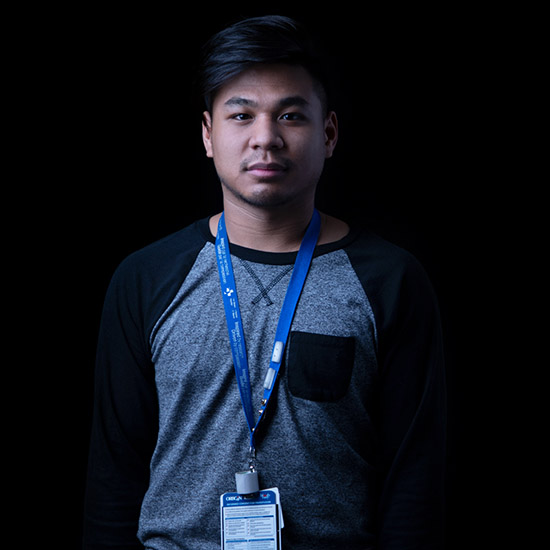

— Michael
— Jeannette
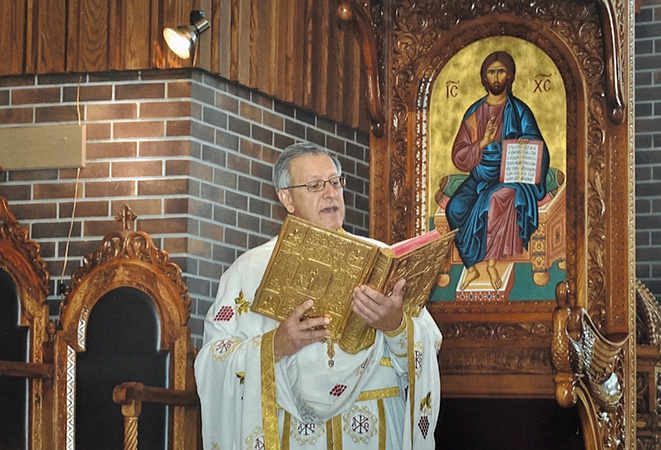
COVID-19 patient grateful for compassionate care
One of the patients, who experienced firsthand compassionate care on the COVID-19 floor, was Fr. Alex Michalopulos. The Greek Orthodox priest spent 10 days in our hospital. He couldn’t be more thankful to be feeling better today. “For the times when the doctors or nurses came in to see me, for the times when I was reassured—I’m thankful I was well taken care of with love and respect for human life.”
“I have a lot more respect for the medical professionals. I always had, but this time it was at a different level. They were there for me.” – Fr. Alex Michalopulos

As tears well up in his eyes, and he stops briefly to regain his emotions, Fr. Michalopulos says it’s sometimes good to be on the other side, to feel what others are going through. “I have a lot more respect for the medical professionals. I always had, but this time it was at a different level. They were there for me.”
He adds, “They held my hand. They showed compassion. They showed a lot of respect and love. I will be forever grateful for them.” It was that special touch, and care from complete strangers that helped give Fr. Michalopulos the strength to get back home to the family he loves and eventually to his parish family.
“I will always remember how I was treated by strangers. I admire them and will always pray for them.”
In an effort to do his part to help, Fr. Michalopulos is participating in research that is investigating the long-term effects of the virus. Drs. Sara J. Abdallah and Juthaporn Cowan are checking in on participating patients, like Fr. Michalopulos at three, six, and 12 months after they were initially infected.
He explains why it was important to become involved. “I thought it would be useful to help researchers understand the effects and lingering effects of the virus in gathering information to help create a vaccine and or a cure.”
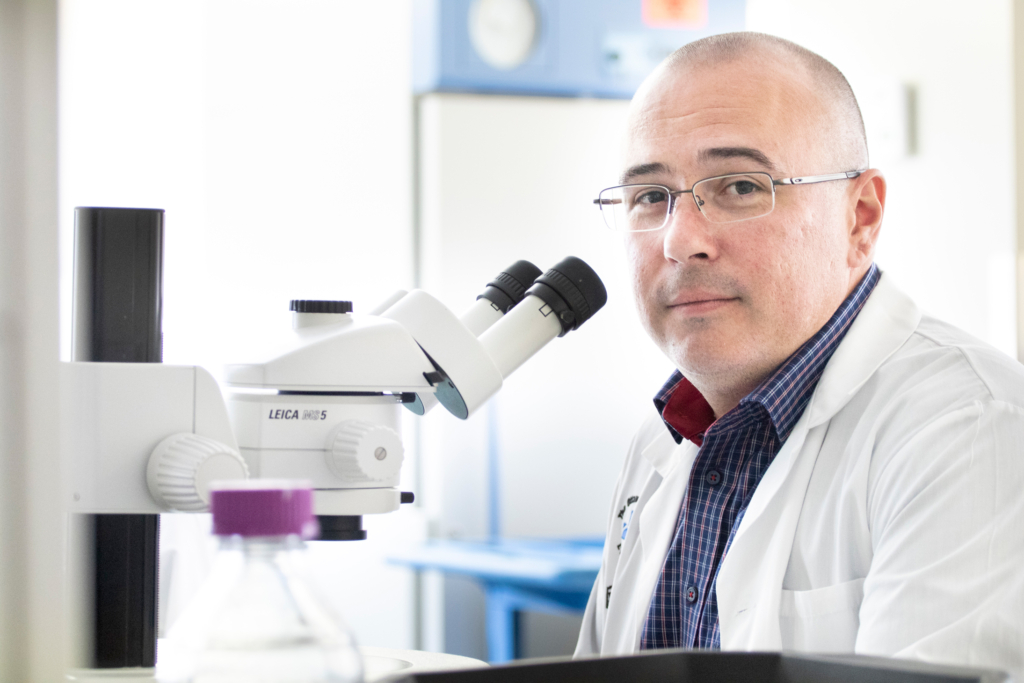
Giving back through research
Researchers at our hospital have been deeply involved in the global race to combat COVID-19. They are exploring more than 60 research projects to support the worldwide effort to find better ways to treat and prevent the virus. A number of those projects have been supported by donors through the COVID-19 Emergency Response Fund, including a world-first clinical trial, led by Dr. Rebecca Auer, which aims to protect cancer patients from COVID-19 – to date, 22 patients, have been recruited.
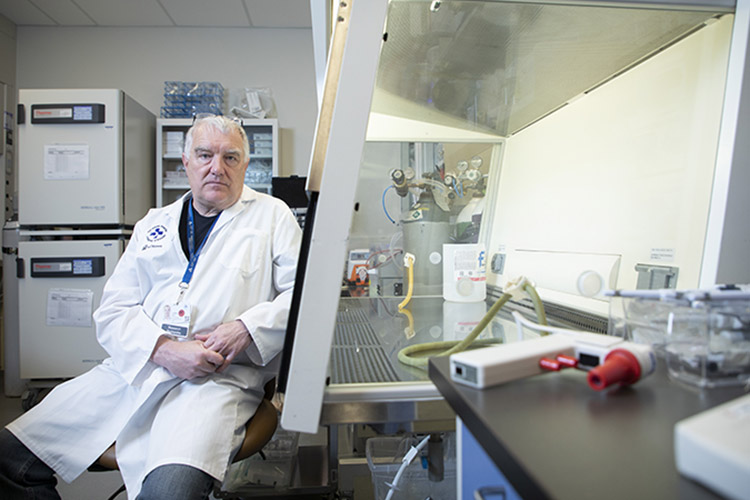
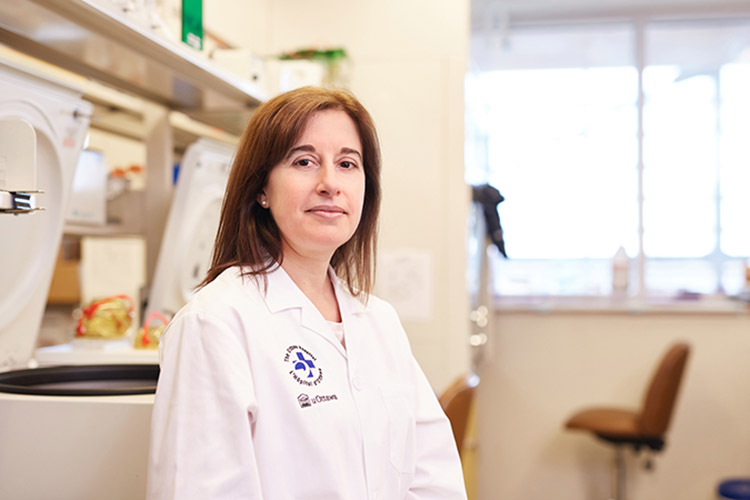


Drs. John Bell and Carolina Ilkow are harnessing their expertise in making cancer-fighting viruses to develop a vaccine against COVID-19 — a made-in-Canada solution. In addition, our Biotherapeutics Manufacturing Centre is helping to manufacture three other COVID vaccines for clinical trials, as well as an experimental stem cell therapy.
Pushing forward despite a challenging year
As research continues to produce more answers and vaccines continue to roll out across the region, the team caring for patients remains steadfast. “The vaccine brings us hope. I remember how exciting it was when I received mine,” says Kristine.
There is hope someday they can start getting back to the way things used to be, or at least close to it. For Kristine, it would mean not worrying about hugging her children when she comes home from work.
For Leah, it would mean letting her mind shut off for the first time in a year – and truly relax. For Vanessa, it would mean the excitement of spending time with her fiancé, Colin – also a frontline worker – as they’ve been isolated from each other during the pandemic. Despite the challenges, each one takes great pride in the care they’ve been able to provide during these unprecedented times. And how they also helped each other along the way.
Check out Pulse Podcast to hear more about a year of working on the COVID floor.
The Ottawa Hospital is a leading academic health, research, and learning hospital proudly affiliated with the University of Ottawa.